vcluster loft-sh
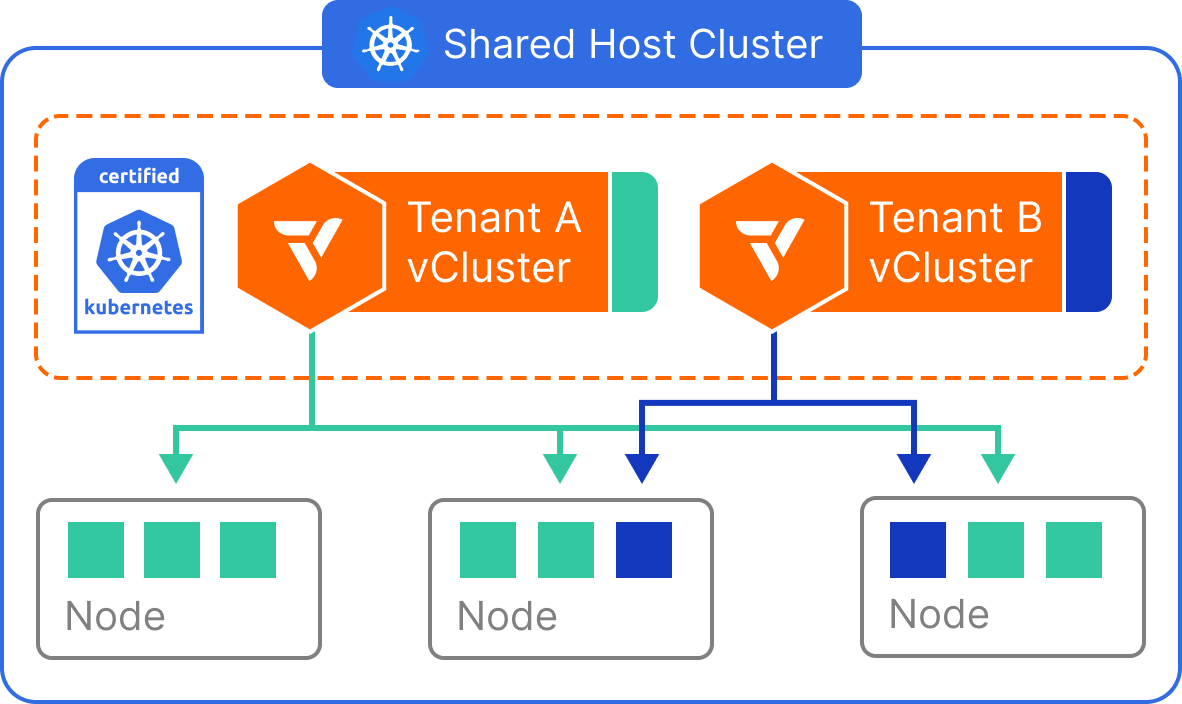
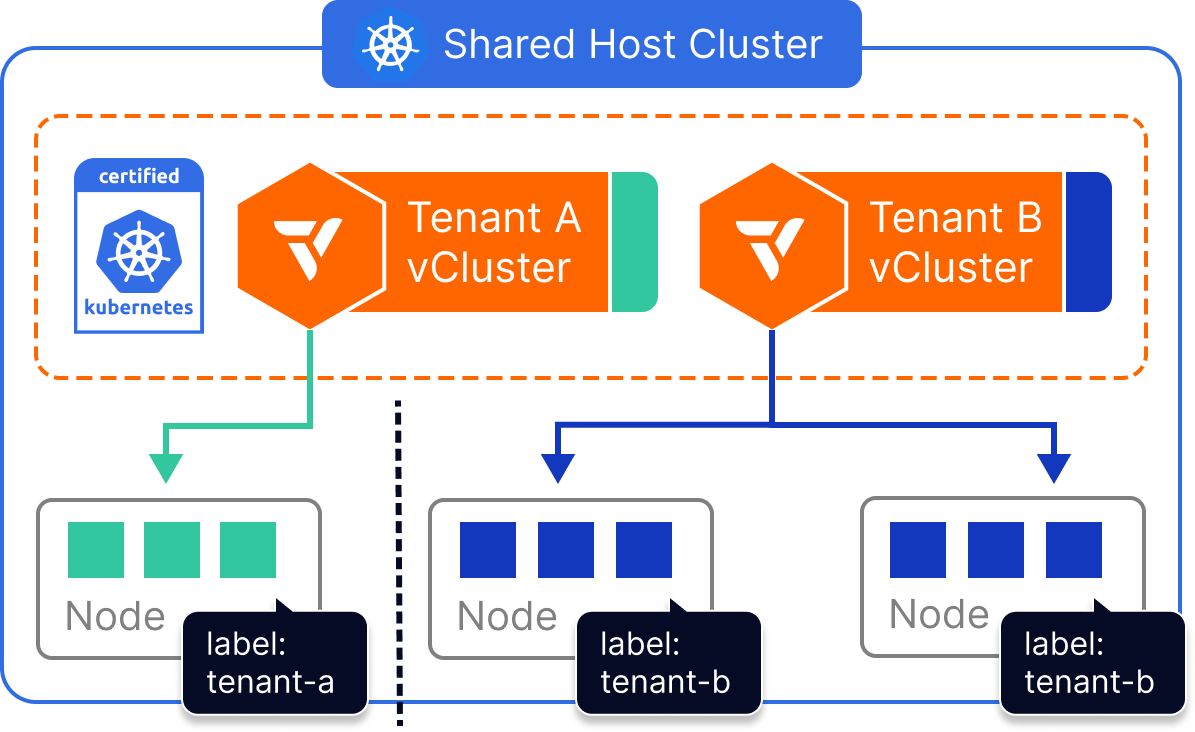
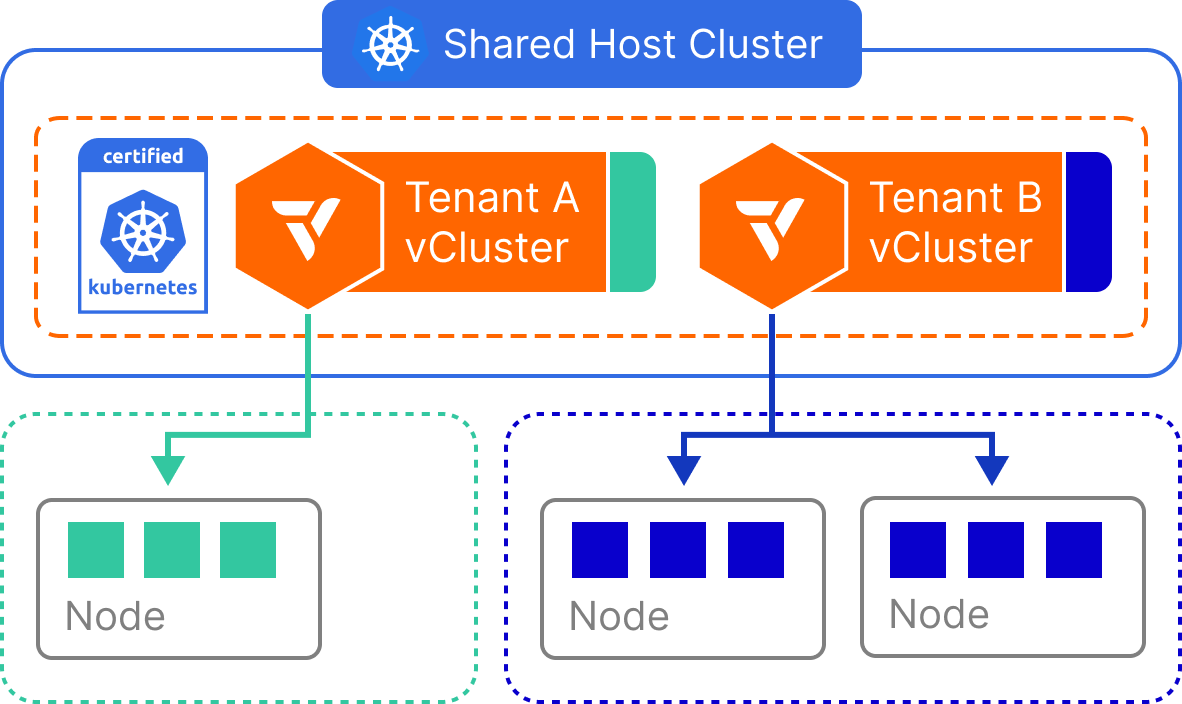
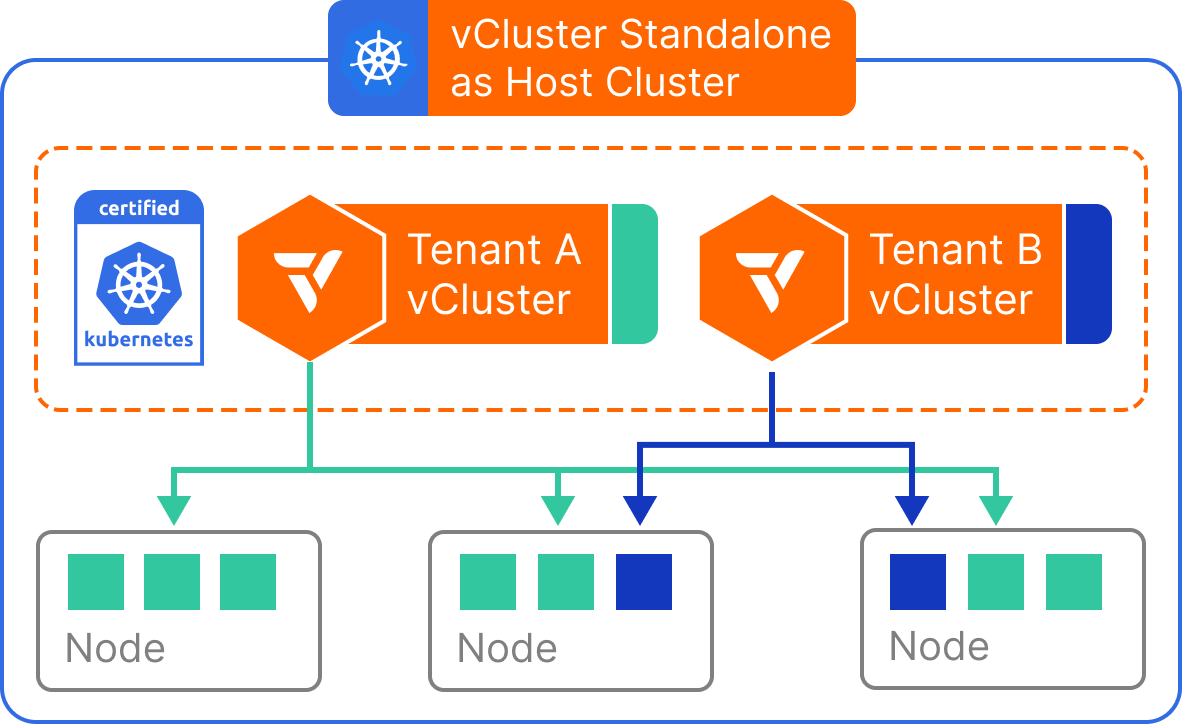
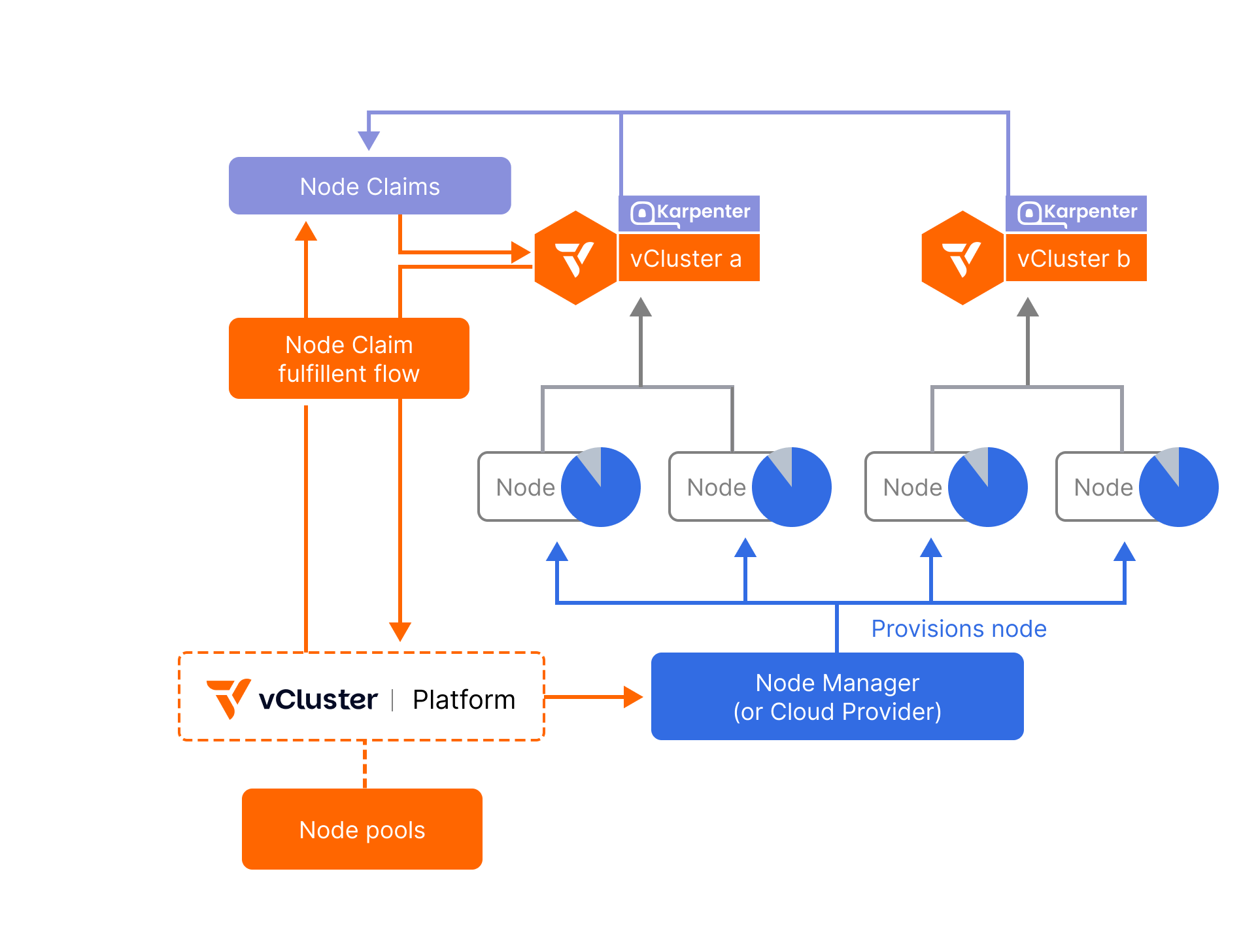
winget install --id=loft-sh.vcluster -e vCluster is a Kubernetes virtualization platform designed to create fully functional virtual clusters within existing namespaces. This tool allows users to run multiple isolated Kubernetes environments on a single host cluster, enhancing multi-tenancy and isolation while reducing costs compared to separate full clusters.
Key Features:
- Isolation and Multi-Tenancy: Each vCluster operates in its own namespace, providing strong isolation for enhanced security and resource management.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces infrastructure expenses by utilizing shared resources instead of dedicated clusters.
- Security and Isolation: Offers granular permissions and an isolated control plane, minimizing risks associated with privileged access.
- Flexibility in Environments and Storage: Supports various Kubernetes versions and distributions, along with adaptable backing stores like SQLite or etcd for scalability needs.
- Scalability Enhancements: Reduces API server load through independent management of CRDs within each cluster.
Audience & Benefit: Ideal for platform engineers, DevOps teams, cloud providers, and organizations requiring scalable Kubernetes solutions without high infrastructure costs. vCluster enables secure, efficient multi-tenant deployments, allowing teams to manage resources independently with reduced complexity and overhead.
This tool is installed via winget, offering a seamless setup process.